Leishenshan bows out
By Liu Caiyu and Wan Lin Source:Global Times Published: 2020/4/15 23:23:40

Aerial photo taken on April 14, 2020 shows ambulances transferring the last batch of COVID-19 patients to other hospitals at Leishenshan (Thunder God Mountain) Hospital in Wuhan, central China's Hubei Province.Photo:Xinhua
Following the bow of Leishenshan Hospital director at the ceremony on Wednesday, the makeshift hospital in Wuhan embraced a phased-victory curtain call after a 67-day battle against the COVID-19.
"Like a stone finally fell to the ground," the hospital head Wang Xinghuan said, as he bowed and thanked all who fought alongside against the virus outbreak. Leishenshan Hospital recorded a low death rate among the hospitalized patients and no medical staff or volunteers was infected.
Since receiving the first batch of COVID-19 patients in February, more than 3,000 medical staff from 16 medical support teams across the nation had worked at the makeshift hospital.
A total of 2,011 patients had received treatment there with about 1,000 severe and critical patients. The overall death rate is 2.3 percent.
After closure, the Leishenshan's facilities will be mothballed, rather than being dis-mantled immediately. The hospital needs to hand over its remaining patients to the local Wuhan Donghu Hospital.
Wang Peiyu, deputy head of Peking University's school of public health, told the Global Times on Wednesday that "since the pandemic is still severe worldwide, China cannot let down the guard. The makeshift hospital should be in preparation for the long-term fight against the virus."
Now, Suifenhe port in China's Heilongjiang Province bordering Russia is building makeshift hospitals mainly to treat imported cases, local infections by the imported cases and asymptomatic patients, which could help avoid a potential se-cond wave of the outbreak in China, Li Kun, an official from the Leishenshan told media on Tuesday. "So we have to mothball the Leishenshan in case of further use."
Leishenshan was built following the example of the Xiaotangshan Hospital in Beijing, a makeshift hospital built to treat patients during the 2003 SARS outbreak.
Xiaotangshan was also not being immediately dismantled after the end of SARS and its inpatient wards were not torn down until 2010 and it was used as a rehabilitation center since 2012, media reports said.
Both the closure of Leishenshan and the Wednesday departure of a medical team from Peking Union Medical College Hospital, the last batch of the medical team who supported Wuhan during its hardest time of the epidemic, marked the phased victory against the coronavirus in China, experts said.
The number of current confirmed cases in Wuhan has dropped below 200 as of Wednesday.
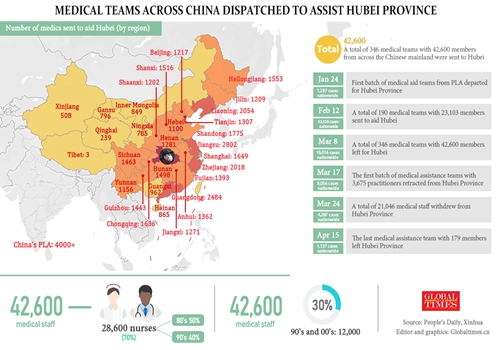
Medical teams across China dispatched to assist Hubei Province. Photo: GT
Maintaining gains
As of Tuesday, China has reported a total of 6,746 cases of asymptomatic infections, 1,297 of whom were later diagnosed as confirmed patients.
To further seek asymptomatic infections and its capability of infectivity, China has been conducting an epidemiological survey in Wuhan, as well as in other nine provinces and cities, including Beijing, Shanghai, South China's Guandong Province, and Central China's Hubei Province.
Wang told the Global Times "making the preparation of a long-term fight against the epidemic doesn't mean there will be a second outbreak."
The current epidemiological survey and some antibody tests conducted in some cities will help medical experts to have more thorough understanding on the epidemic in China, Wang said, noting enterprises, communities and everyone should behave themselves and take actions to prevent the virus spread as China gradual resumes work and production.
Communities, fever clinics and epidemiological surveys, which are dubbed as three lines of defense, should be well guarded, officials at the NHC said.
Though the epidemic ebbs in the country, regions that were previously hit hard by the virus keep up with the efforts to contain the outbreak by conducting COVID-19 tests on people that are highly suspected to be infected and potential virus carriers.
In Hubei, cities such as Yichang have provided free nucleic acid tests to passengers from Wuhan and other high-risk regions at the train stations and the airport. Qianjiang and Xiangyang opened the tests to the public with a certain amount of fees charged.
Some enterprises in Huanggang reached by the Global Times said they had car-ried out COVID-19 tests for all returned employees before their work resumption.
Posted in: SOCIETY