HOME >> SOURCE
Policymakers find keys to auto growth
By Zhang Hongpei Source:Global Times Published: 2019/12/17 19:38:40
Crucial period for industry adjustment, consumption recovery has come: analysts

Tesla vehicles park outside a building in Beijing in November. Photo: Zhang Hongpei/GT
The slumping trend of China's auto sales is likely to continue through the end of 2019 with industry analysts estimating a negative growth of around 8 percent. Analysts suggest it is high time for top policymakers, industry players and consumers to help collectively reshape the sector's future.
Based on weakening auto sales during the first 11 months of this year, which fell 9.1 percent on a year-on-year basis to 23.11 million units, Xu Haidong, assistant secretary general of the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers (CAAM), told the Global Times on Monday that the full year is likely to witness a negative growth rate of 8 percent.
Retail sales of passenger vehicles stood at 1.94 million units in November, down 4 percent year-on-year, putting the slip in the first 11 months at 8 percent, according to the China Passenger Car Association (CPCA).
China encountered a contraction in auto sales for the first time last year since the 1990s when it slid 2.8 percent year-on-year to 28.08 million units.
"The core reason behind is damaged consumption power for people living in small cities and towns where rising living costs such as robust home prices have affected their purchase confidence amid the economic downward pressure," Xu noted.
The trade war between China and the US also played its role by somewhat affecting operation of middle-sized and small enterprises, he added.
Given the current low speed of development for China's auto sector, Xu estimated a sales rebound would occur around 2022 when purchasing power recovers.
According to a research by the Development Research Center of the State Council, sales in county-level cities, which account for nearly 30 percent of total auto sales in the country, have witnessed an obvious slump in the first half of this year. Car models priced less than 100,000 yuan ($14,301), taking up 40 percent of market share, registered a negative growth of 23 percent. By contrast, sales of luxury car brands have increased despite the overall slowdown.
Liu Shijin, deputy head of the economic committee of the 13th Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference National Committee, said in a forum last week that a deeper reason behind weak auto sales is the expanding income gap between the rich and poor.
"The market needs to help restore consumer's confidence especially those in the county-level cities or rural areas, which make up a bulk portion," Cui Dongshu, secretary-general of the CPCA, told the Global Times on Monday.
The CPCA expected the market to warm up faster this month as first-time car buyers are likely to make the purchase before the Chinese New Year, which falls in January 2020.
China has vowed various measures to boost auto consumption this year. A key document published by the State Council in September suggested municipal authorities ease restrictions on car purchases to support auto sales.
Driven by a string of policies intend to stabilize employment, finance, foreign trade, investment and market expectations, the drop in auto sales and rate of production is narrowing on a monthly basis.
Data from the CAAM showed that November witnessed a month-on-month increase of auto production by 13 percent and sales by 7.7 percent.
Industry analysts expect the drop in auto production and sales will shrink as the market gradually stabilizes, guided by public policy.
From the perspective of car ownership, there is huge potential for China's auto sector to grow, Cui noted.
Compared with the ownership ratio of 800 cars per 1,000 persons in the US, and 600 cars per 1,000 person in Europe and Japan, the current ratio for China is merely around 170, demonstrating space for development.
Despite the sales drop, a round of opportunities and challenges are helping readjust China's auto sector. "2019 is a crucial year of transformation as the business model relying on high price-performance ration might not sustain for domestic automakers' future growth. They need to know the market better and improve where they are not strong enough to fully compete with joint ventures and foreign brands," Xu noted.
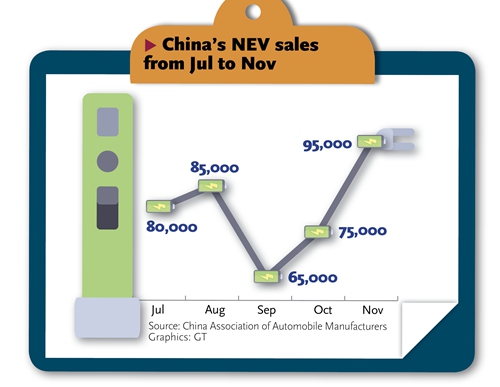
Photo: GT
NEV hits the road
Since the scaling back of government's incentives, the new energy vehicles (NEV) segment has slid for five consecutive months. In November, sales of NEV fell 43.7 percent, the CAAM said, following a 45.6 percent drop in October.
In the first 11 months of the year, sales of NEV recorded a year-on-year growth of 1.3 percent to 1.04 million units. Last year, NEV sales jumped almost 62 percent year-on-year even as the broader auto market contracted.
Cui estimated that sales of NEV would increase by 2-3 percent this year.
China has been revving up development of green and smart vehicles in spite of the sluggish auto market.
Sales of NEVs are expected to make up about 25 percent of the total new car sales by 2025 and intelligent connected vehicles up to 30 percent, according to a draft plan released by the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology earlier this month.
"So far, China's NEV sector has not entered a very sound development track since it has just waved goodbye to the subsidy era. The market should involve more competitive automakers, which can genuinely bring down costs to compete with traditional combustion cars," Cui remarked.
"Domestic auto brands should also seek their strategic positioning in competing with foreign players. They need to take advantage of the complete supply chain that has accumulated for decades in China's auto industry, which can help reduce costs," he added.
Foreign automakers have shown signs of making China a key battleground.
US electric carmaker Tesla obtained a mass production license in its Shanghai Gigafactory in November, aiming to produce more than 500,000 cars a year. German carmaker Volkswagen is preparing to launch two Chinese factories with a production capacity of 600,000 vehicles to make electric cars for 2020, according to media reports.