Xi to attend ceremony marking completion of BeiDou-3 system as final satellite starts operation in network

Beidou Screenshot
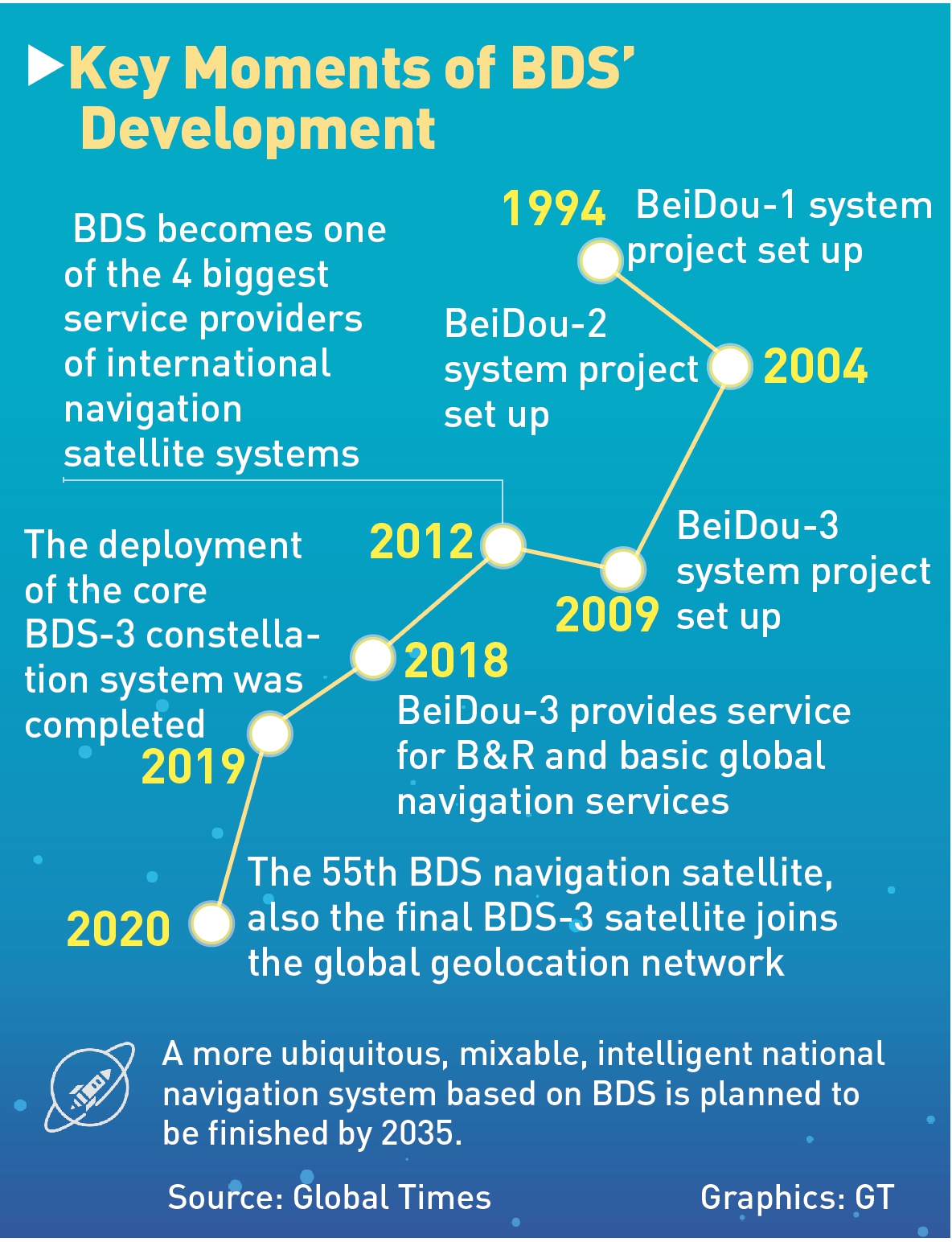
Chinese President Xi Jinping will attend a ceremony marking the completion and launching of the BeiDou-3 Navigation Satellite System scheduled for Friday in Beijing.According to the China Satellite Navigation Office on Wednesday, the final satellite of the third generation of China's BeiDou navigation satellite system, or the BDS-3, has completed in-orbit tests and assessment work, and officially joined the network.
Xi, also general secretary of the Communist Party of China Central Committee and chairman of the Central Military Commission, will be present at the Friday ceremony at the Great Hall of the People, which will start at 10:30 am, the Xinhua News Agency reported.
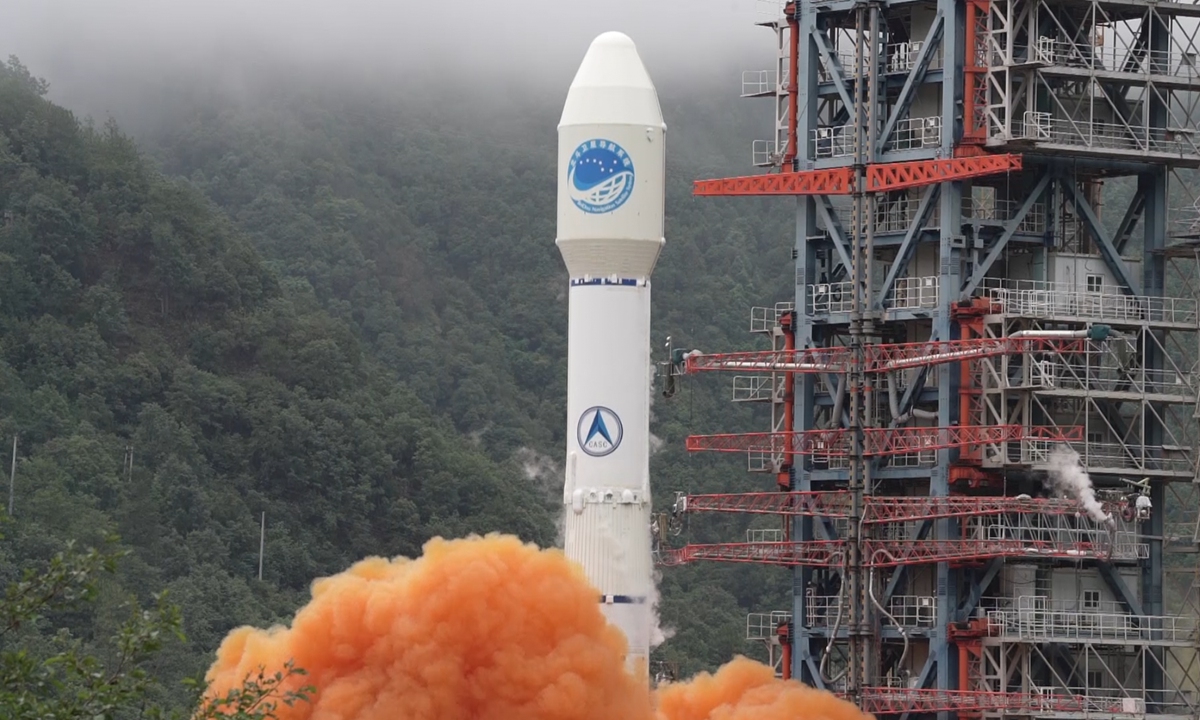
The satellite is also the 55th member of the BeiDou system that was launched by a Long March-3B launch vehicle from the Xichang Satellite Launch Center in Xichang, Southwest China's Sichuan Province on June 23.
The satellite will start providing navigation, positioning and timing services, the office said on Wednesday.
A BDS insider with the Xi'an Satellite Control Center told the Global Times on Wednesday that the final BDS-3 satellite reached the fixed service point in the GEO orbit that is about 36,000 kilometers above ground on June 30.
The satellite will provide quality services for more than a decade to come, the insider noted.
The final BDS-3 satellite is the third geostationary Earth orbit (GEO) satellite and 30th of the third-generation series of BDS-3, and was developed by the China Academy of Space Technology under state-owned space giant China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC).
BDS is China's largest space-based system and one of the four global navigation networks. The three others are the US' GPS, Russia's GLONASS and the European Galileo.
Compared to previous generation series, the BDS-3 constellation with an array of 30 satellites on three different orbit planes - three at the GEO, three at the inclined geosynchronous orbits, and 24 at the medium Earth orbit--have a higher bandwidth, allowing for enhanced communication, and carry more accurate and stable atomic clocks to improve timing and navigation services, according to the project contractor, China Academy of Space Technology.
This year, China's BDS has been playing an important role in providing mapping services for the rapid construction of Huoshenshan, Leishenshan makeshift fangcang hospitals in Wuhan, Central China's Hubei Province at the beginning of the year when the city was stricken by the most severe COVID-19 outbreak in the country.
Also, BDS terminals were carried atop Qomolangma (Everest in English) for the first time in late May, to assist the Chinese surveying team in their quest to measure the new height of the world's peak.
Graphics: GT


