SOURCE / INDUSTRIES
GDP growth seen at 2% in 2020 and 7% in 2021, but risks remain

Cars made in China wait for shipment at a port in Lianyungang, east China's Jiangsu Province, July 16, 2020. China's economy bounced back to growth in the second quarter this year as the country gradually resumed work and production after having the COVID-19 epidemic effectively contained, official data showed Thursday. The country's gross domestic product (GDP) expanded 3.2 percent year on year in the second quarter, according to data from the National Bureau of Statistics (NBS). (Photo by Wang Chun/Xinhua)
China's economy may achieve 2 percent growth this year, as a result of rapid business resumption and the government's supportive policies.
The growth could rise to 7 percent next year, experts said, with factors such as containment of the coronavirus pandemic, international business environment and China's economic policies all playing a role.
These predictions are in line with the new figures released on Thursday by rating agency Moody's Investment Service, which said China's GDP growth will return to above 7 percent in 2021 from 1.9 percent in 2020.
The Moody's report said that if the economic shock is more severe and longer-lasting, regional and local governments will encounter pressure on finances to maintain employment and social stability.
The economy is weaker this year than in previous years. But given the global COVID-19 outbreak, China - which was also hit hard by the disease - has recovered more quickly than most countries due to its huge consumption market.
But there are growing uncertainties about the outlook for growth.
"We are confident about the domestic market because of its huge size, but we don't expect a 1.9-percent growth rate this year, nor 7 percent next year, because the epidemic had a marked impact in the first half. The ongoing epidemic in many other countries, including China's major trading partners, and overseas protectionism may all affect trade," Zhuang Rui, a deputy dean of the University of International Business and Economics' Institute of International Economics in Beijing, told the Global Times on Sunday.
The IMF has estimated that the US will report a GDP contraction of 5.9 percent in 2020 and Japan will see a contraction of 5.2 percent, while China is likely to achieve an expansion of 1.2 percent.
Wang Jun, an expert at the China Center for International Economic Exchanges in Beijing, told the Global Times that Moody's prediction matches China's actual development and is similar to that of the IMF, thanks to the fast business and investment rebound as the epidemic was brought under control. This situation has won back the confidence of international enterprises in the Chinese market.
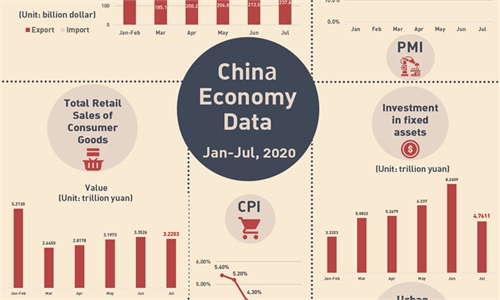
In the first seven months of this year, actual foreign investment in China reached 535.6 billion yuan ($78 billion), up 0.5 percent year-on-year, and a 15.8 percent month-on-month increase compared with June, Zong Changqing, director of the department for foreign investment under the Ministry of Commerce, said at a press conference on August 13.
Customs data also showed that In July, China's foreign trade reached 2.93 trillion yuan, up 6.5 percent year-on-year, with exports up 10.4 percent and imports up 1.6 percent.
"I believe that China's GDP growth can reach 2 percent this year," Wang said, but whether it can reach 7 percent next year will depend on the government's policies.
If policies are looser, growth will be higher next year, Wang said.