NASA extracts breathable oxygen from thin Martian air
NASA extracts breathable oxygen from Martian air
NASA has logged another extraterrestrial first on its latest mission to Mars: converting carbon dioxide from the Martian atmosphere into pure, breathable oxygen, the US space agency said on Wednesday.

"MOXIE isn't just the first instrument to produce oxygen on another world," Trudy Kortes, director of technology demonstrations within NASA's Space Technology Mission Directorate, said in a statement. She called it the first technology of its kind to help future missions "live off the land" of another planet. The instrument works through electrolysis, which uses extreme heat to separate oxygen atoms from molecules of carbon dioxide, which accounts for about 95 percent of the atmosphere on Mars. The remaining 5 percent of Mars' atmosphere consists of molecular nitrogen and argon.

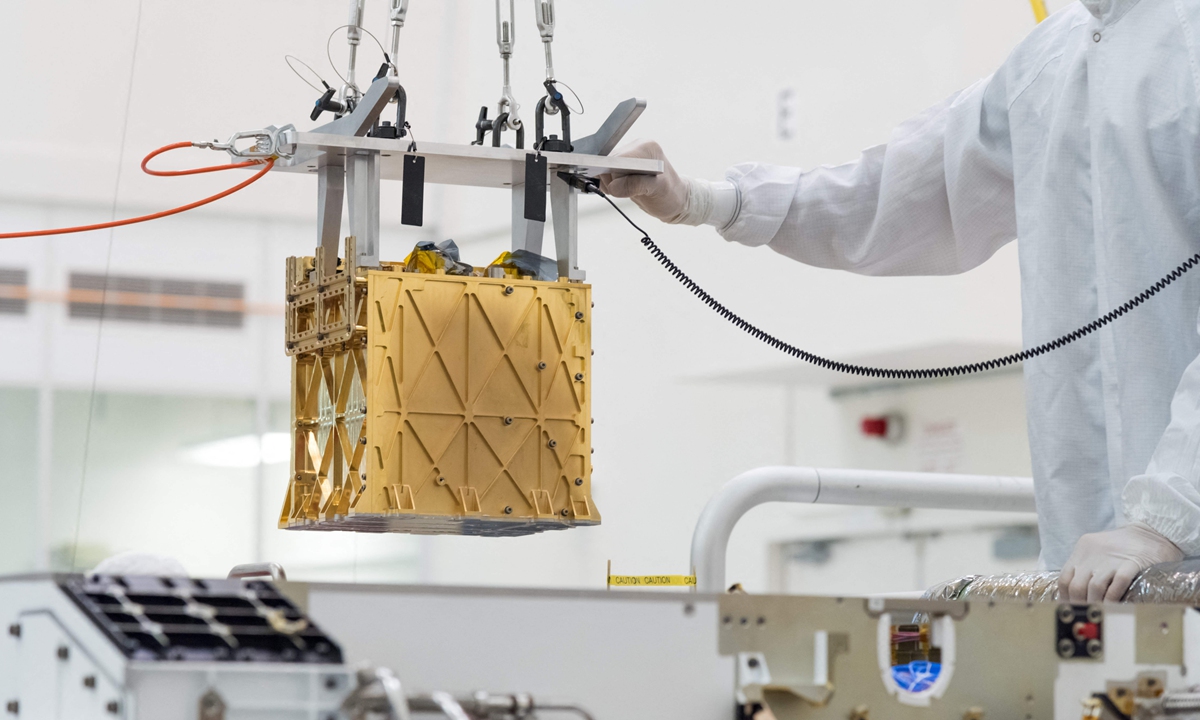
Technicians in the clean room carefully lowering the Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment (MOXIE) instrument into the belly of the Perseverance rover in the cleanroom at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in Pasadena, California in March 2019. Photo: VCG
The unprecedented extraction of oxygen, literally out of thin air on Mars, was achieved Tuesday by an experimental device aboard Perseverance, a science rover that landed on the Red Planet on February 18 after a seven-month journey from Earth. In its first activation, the toaster-sized instrument dubbed MOXIE, short for Mars Oxygen In-Situ Resource Utilization Experiment, produced about 5 grams of oxygen, equivalent to roughly 10 minutes' worth of breathing for an astronaut, NASA said. Although the initial output was modest, the feat marked the first experimental extraction of a natural resources from the environment of another planet for direct use by humans."MOXIE isn't just the first instrument to produce oxygen on another world," Trudy Kortes, director of technology demonstrations within NASA's Space Technology Mission Directorate, said in a statement. She called it the first technology of its kind to help future missions "live off the land" of another planet. The instrument works through electrolysis, which uses extreme heat to separate oxygen atoms from molecules of carbon dioxide, which accounts for about 95 percent of the atmosphere on Mars. The remaining 5 percent of Mars' atmosphere consists of molecular nitrogen and argon.