Broader US chips export curb to propel Chinese replacement in autonomous driving: experts
US intends to keep China at lower end of industrial chain forever: official
chip Photo:VCG
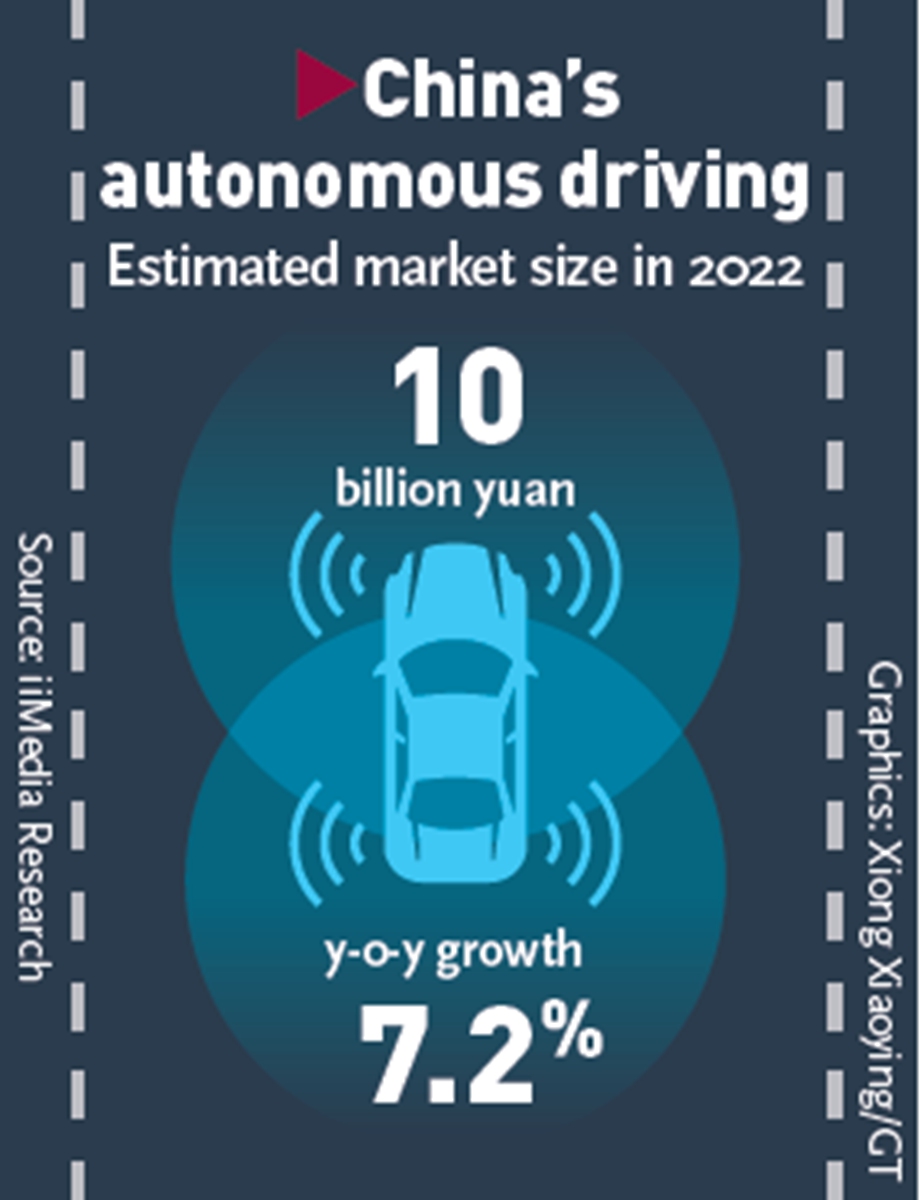
Market
China's fast-growing autonomous driving sector could be the latest target under a broader US ban on exports to China. But experts said frequent US technology crackdowns have pushed local companies to accelerate research and development of domestic replacements.
A broader curb on US shipments to China of chips used for artificial intelligence (AI) and chipmaking tools, which apply to Nvidia Corp, a major chip supplier for China's autonomous vehicles, is likely to slow down China's fast-growing autonomous driving industry, VOA reported on Tuesday.
The US Commerce Department sent letters to three US companies -- KLA Corp, Lam Research Corp and Applied Materials Inc -- forbidding them from exporting chipmaking equipment to Chinese factories that produce advanced semiconductors with sub-14 nanometer processes, unless they obtain Commerce Department licenses, Reuters reported on Sunday.
The rules would also force Nvidia to halt shipments of top AI chips known as A100 and H100 to Chinese companies unless it obtains licenses, according to the report.
Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesperson Mao Ning said on Tuesday that the broader US curbs on AI chips and chipmaking tools amount to pure hegemony in science and technology.
The US wants to use its science and technology advantages to keep China and other developing countries at the lower end of industrial chain forever, which is not constructive, Mao said.
The main applications of the chips banned this time involve AI computing. In the automotive industry, such chips are mainly used in training the models for self-driving and in data centers, Zhang Xiang, visiting professor of the Engineering Department of the Huanghe Science and Technology University, told the Global Times on Tuesday.
"Without the models, the level of autonomous driving cannot be improved, which is what the US government intends," Zhang said.
Ma Jihua, a veteran technology industry observer, told the Global Times that the latest move showed that the previous crackdowns on China's technology sector had not worked well, and the decoupling would disturb the market order and hurt the normal operation of companies.
Nvidia expects it could lose $400 million in potential chips sales to China.
"We are working right now with our China customers to provide them alternative product versus the A100," Colette Kress, CFO of Nvidia Corp, said at the Goldman Sachs 2022 Communacopia + Technology Conference on Monday.
Nvidia's chips are among the most advanced in autonomous driving, but the pace of Chinese-made alternatives is accelerating with more financing and technological breakthroughs as Chinese firms rush to increase self-sufficiency.
Horizon Robotics, a Chinese company that offers AI computing platforms for intelligent vehicles, in June said that it had secured investment from FAW group, which will be used to augment research on AI chips.
As an example of domestic intelligent driving chips, Horizon has launched the Journey 5, a high-performance automotive AI processor optimized for advanced autonomous driving applications. It features high power efficiency reaching up to 128TOPS (trillion operations per second) and supports L4 high-level autonomous driving.
In April, Horizon said it had reached a cooperation agreement with Chinese carmaker BYD to carry the Journey 5 chip in some of its models.
Another autonomous chip producer, Black Sesame Technologies, announced on August 8 that it had completed C+ round financing that raised more than $500 million.
"These successful examples show that domestic replacements for autonomous driving chips are gaining pace, though they still need to show they have the financial and technical capacity to compete with foreign top players," Zhang said.
China's autonomous driving sector has entered the fast lane. By 2030, the vehicles will account for 60 percent of the ride-hailing market, according to a report issued by IHS Markit in 2021.



