Scientists find hints of new source of water in lunar soil samples from Chang’e-5 mission
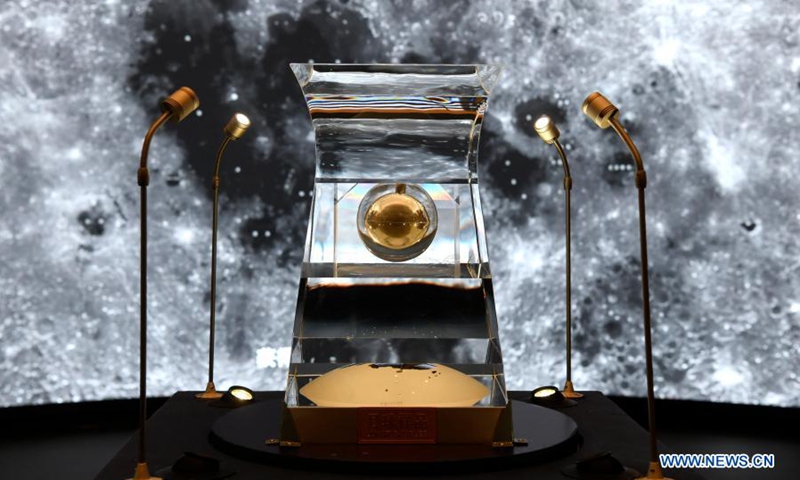

The lunar samples No. 001 brought back by China's Chang'e-5 probe is displayed at the National Museum of China in Beijing, capital of China, February 27, 2021. Photo: Xinhua
Chinese scientists and their international partners have learned more about the moon after studies and research into lunar soil samples from the Chang'e-5 (CE-5) mission. In the two latest discoveries, researchers found hints of a new source of water on the moon for future explorers and revealed the activities of young basalt on the moon.
The Chang'e-5 mission brought 1,731 grams of lunar minerals back to Earth. The landing site in the Northeastern Oceanus Procellarum basin of the moon was considered to have one of the youngest basalt units on the lunar surface with rich heat-generating elements such as uranium, thorium and potassium.
In a report published in Nature on Monday, Chinese researchers and their partners in the UK report the abundance, hydrogen isotope composition and core-to-rim variations of water measured in 32 impact glass beads extracted from lunar soil returned by the Chang'e-5 mission.
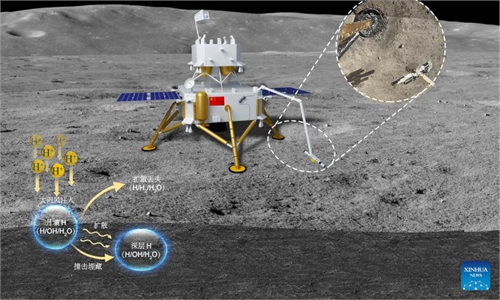
Impact glass beads are major components of lunar soil. But the water inventory of impact glass beads has not yet been investigated in detail, despite these glassy beads being potential candidates for playing a significant role in a lunar surface water cycle. To investigate this possibility, scientists carried out a systematic characterization of the petrography, major element composition, Raman characteristics, water abundance and hydrogen isotope composition on the impact glass beads returned by the CE5 mission, aiming to identify and characterize the missing water reservoir on the moon's surface.
Scientists estimate that the amount of water hosted by impact glass beads in lunar soils may reach up to 270 trillion kilograms. "Our direct measurements of this surface reservoir of lunar water show that impact glass beads can store substantial quantities of solar wind-derived water on the moon and suggest that impact glass beads may be water reservoirs on other airless bodies," according to the report.
Hui Hejiu, a professor at Nanjing University, told the media that in the future deep space exploration by human beings, impact glass beads may be used as a candidate water source to provide supplies when the efficiency of collecting glass beads and extracting water is high.
In another report published by Astrophysical Journal Letters in early March, Chinese scientists said they combined Fe and Mg isotope analyses with a comprehensive study of petrology and mineralogy on two CE-5 basalt clasts, the Global Times learned from the Nanjing-based Purple Mountain Observatory under the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
CE-5 basalts are the most evolved basalts to date on the moon.
"Our new Fe-Mg isotope data indicate that the young CE-5 mare basalts possess a hybrid mantle cumulate source that incorporates both early- and late-stage LMO cumulates, which may play an important role in the generation of the late lunar volcanism," read the article.
Global Times